Table of Contents
SaaS businesses have transformed how companies operate, offering cloud-based solutions accessible from anywhere. This growth is projected to continue, with the SaaS market estimated to reach $307.3 billion in 2026, indicating the significant and growing role of SaaS in the modern business landscape.
But what's the organizational structure behind these SaaS startups?
Let's take a look at their inner workings, exploring how they're structured, their key departments, and the trends and challenges shaping their design.
TL;DR: SaaS Company Org Structures
-
Most SaaS companies follow a hierarchical, flat, or matrix structure
-
Key departments include product, sales, marketing, and customer success
-
Product teams rely on agile methods and user feedback to improve fast
-
Sales and marketing need CRM alignment to drive efficient growth
-
Support teams reduce churn with strong onboarding and retention plays
-
Remote work and agile frameworks are shaping modern SaaS structures
-
Growth, scalability, and uptime are constant challenges for SaaS teams
What does the organizational structure of a SaaS company look like?
Hierarchical Structure in a SaaS Company
SaaS companies often adopt a hierarchical organizational chart, a familiar structure where authority flows from the top and it's easy to define roles and responsibilities. The CEO (or founder) is responsible for shaping the company's vision and direction, and also ensuring everyone's dedication to the company's mission.
Rounding out the c-suite, the Chief Marketing Officer (CMO), Chief Operating Officer (COO), and Chief Financial Officer (CFO) each oversee key domains like marketing, operations, and finances.

Further down, department heads or managers take charge of specific realms—sales, marketing, product development, customer support—executing strategies within their areas. They report to top-level executives, ensuring alignment with the company's overarching goals. Within these departments, teams collaborate to fulfill their respective objectives, organized either by function or project needs. The hierarchy ensures clarity in roles and responsibilities, promoting accountability within each team.
While this traditional structure offers clarity, it can sometimes affect innovation and adaptability. Its top-down nature might suppress creativity and hinder swift responses to market shifts. To thrive in the current tech landscape, SaaS companies must blend hierarchy with flexibility, striking a balance that fosters innovation and agility.
Flat SaaS Company Organizational Structure
In some SaaS companies, they go for a flat organizational structure, aiming for minimal layers of management and a decentralized decision-making process.

This approach nurtures a collaborative atmosphere, giving employees more freedom and responsibility. With fewer management levels, there's a push for everyone to think creatively and take charge of their tasks.
Plus, decision-making is spread out among employees throughout the organization. This not only empowers individuals but also ensures that decisions come from those who truly understand the situation on a granular level.
Yet, there are hurdles in this flat structure. Without those clear reporting lines, it can get a bit murky for employees. In a traditional setup, you know who's in charge and where to turn for what. But in a flat setup, it might not be as clear, leading to some potential clashes along the way.
Matrix Structure in a SaaS Company
Another option for a SaaS company structure is a matrix structure, a setup where employees answer to both functional departments and specific project teams.
It's a system that's great for optimizing resources, leveling up skills and knowledge, and fostering teamwork. Yet, it also introduces some complexity. Juggling between two reporting lines means employees need to have great time management to ace both their functional duties and project commitments.
What are the key departments in a scalable SaaS company structure?
Product Development in a SaaS Company
At the core of every SaaS product lies the team responsible for crafting, building, and maintaining the software that customers rely on. It's a team effort, with software engineers, designers, and quality assurance pros in the mix.
Within the product development department, agile methodologies are often used to promote iterative and collaborative development. Scrum or Kanban frameworks enable teams to quickly respond to customer feedback and market demands, ensuring that products stay competitive and relevant.
Software Engineers
Software engineers play a crucial role in product development as they're responsible for writing the code that brings the software to life. These engineers have expertise in various programming languages such as Java, Python, and JavaScript. They work closely with designers to ensure that the user interface is intuitive and visually appealing.
Designers
Designers in the product development department focus on creating user-friendly interfaces and visually appealing designs. They collaborate with software engineers to understand the technical constraints and possibilities, ensuring that the final product meets both functional and aesthetic requirements. Designers often use tools like Sketch, Adobe XD, or Figma to create wireframes and prototypes.
QA Specialists
Quality assurance specialists are responsible for testing the software applications developed by the product development team. They perform various types of testing, including functional testing, performance testing, and security testing, to ensure that the software meets the highest quality standards. These specialists use tools like Selenium, JUnit, and JMeter to automate testing processes and identify any bugs or issues.
Sales and Marketing in a SaaS Company
Sales Department
Sales Representatives
These professionals form the frontline of engagement with potential clients. They're tasked with understanding client needs, articulating product value propositions, and closing deals. Their proficiency in product knowledge and persuasive communication is pivotal in converting leads into customers.
Account Managers
Once a client is onboarded, account managers step in to nurture these relationships. They act as liaisons between the company and the client, ensuring satisfaction, addressing concerns, and identifying opportunities for upselling or cross-selling additional services or features.
Sales Operations
This segment focuses on optimizing sales processes, integrating CRM systems like HubSpot migrations to ensure smooth transitions and alignment with sales strategies.
Business Development
This team explores new markets, identifies potential partnerships, and crafts strategies to expand the customer base. Their focus is on long-term growth and fostering relationships that can lead to new business opportunities. This is especially important given the increasing adoption of SaaS by small businesses, with 78% reporting that SaaS solutions have become essential to their business.
Marketing Department Within a SaaS Company
Marketers
They're responsible for crafting compelling campaigns, messaging, and content that resonate with the target audience. They employ various strategies ranging from content marketing, email campaigns, social media, to events, with a goal to attract and engage potential customers.
Product Marketing
This subset of marketing professionals specialize in understanding the product's market fit, its value propositions, and translating technical features into customer benefits. They collaborate with both the product and sales teams to ensure alignment in messaging and positioning.
Analytics and Insights
This team utilizes data analytics and market research to understand customer behavior, measure campaign effectiveness, and derive actionable insights to refine marketing strategies. They play a crucial role in decision-making processes by providing data-driven recommendations.
Marketing Operations and Technology
Managing marketing team technologies, such as marketing automation tools, CRM systems, analytics platforms, and ensuring their integration, falls under this purview. They streamline workflows and optimize processes.
Customer Support in the SaaS Company Organizational Structure
The customer success and support teams within SaaS companies play pivotal roles in ensuring customer satisfaction and long-term relationships. They act as linchpins by providing essential support and maximizing the value clients derive from the software.
Customer success managers serve as tailored guides, engaging with customers to understand their unique needs and objectives. They advocate for the customer within the organization, ensuring a seamless alignment between customer requirements and the software's capabilities.
Meanwhile, the support teams address technical questions and troubleshoot issues, ensuring a smooth user experience. Their expertise turns potential challenges into resolved matters, fostering a continuous sense of guidance and assistance.
Beyond reactive solutions, proactive initiatives such as regular check-ins and comprehensive training resources empower users, enhancing their proficiency in utilizing the software effectively.
HubSpot setup slowing down your marketing team?
Get a complimentary HubSpot audit to uncover inefficiencies, clean up bad data, and optimize your CRM for scalable growth.
What trends are shaping modern SaaS company structures?
Remote Teams in the SaaS Company Organizational Structure
The surge in remote and distributed teams within the SaaS landscape marks a significant shift, deeply influenced by the evolving work culture and technological advancements. This transformation, fueled by the growing acceptance of remote work and the rapid evolution of communication technologies, has reshaped the way SaaS companies function.
One of the standout advantages of embracing remote teams lies in accessing a vast, global talent pool as companies now have the freedom to scout for top-notch talent regardless of location. This not only enriches the diversity of skills but also brings in diverse perspectives that can catalyze innovation and problem-solving.
Additionally, there's a financial upside—reduced overhead costs. Operating without the constraints of physical office spaces means savings on rent, utilities, and other overhead expenses. This newfound flexibility translates into better allocation of resources toward strategic initiatives and employee welfare programs.
But, managing remote teams isn't without its challenges. The ability to leverage robust communication tools and establish clear channels for interaction are imperative. Clear expectations and defined deliverables ensure everyone's on the same page, despite physical distances.
Also, nurturing a culture of strong team collaboration is vital for success. Encouraging camaraderie, facilitating regular virtual meetings, and fostering an environment where ideas flow seamlessly are vital ingredients for cohesive and high-performing remote teams.
Agile Methodologies and the Structure of SaaS Companies
Agile methods have changed how SaaS companies build software. Frameworks like Scrum, Kanban, and various other agile methodologies offer a structured yet adaptable approach. They provide the necessary scaffolding for teams to organize their workflows while retaining the flexibility to recalibrate priorities in response to emerging requirements. This adaptive nature allows teams to pivot swiftly, ensuring focus on the most pertinent tasks at any given time.
But it's not just about the technical side. Agile ways bring a teamwork and customer-focused vibe to the company. It's all about everyone working together to deliver real value to customers. This shift is about making sure everyone's on the same page, aiming to surpass customer expectations in a fast-paced world.
What are the biggest challenges in designing a SaaS organizational structure?
Scalability in SaaS Company Growth Models
Scalability poses a significant hurdle as SaaS companies gorw in their early stage and their customer base expands. It's not merely about growth but about aligning operations, infrastructure, and support capabilities to keep pace with rising demands.
Embracing scalable technologies like cloud computing is necessary in handling increased customer needs. These solutions offer the bandwidth required to manage surges without a hiccup as a company grows.
However, beyond the tech, it's about synchronized efforts across teams. Efficient resource allocation ensures that as demands spike, everyone's working in tandem, preserving both product quality and responsiveness to customer needs.
How SaaS Companies Structure for Reliability and Uptime
Keeping a SaaS application running smoothly is no small feat.
SaaS apps need to be up and kicking all the time. Even a minor glitch can cause ripples, affecting user experiences and disrupting business operations. To put this in perspective, downtime can cost businesses an average of $5,600 per minute, underscoring the critical need for robust infrastructure and disaster recovery plans. This constant availability is a big ask and a significant challenge as downtime disrupts workflows, business activities, and, ultimately, profits.
What can we learn from how SaaS companies organize and evolve over time?
Exploring how SaaS company departments work reveals their different setups. Teams like product development, sales, and support drive their success; trends like remote work and agile methods shape how they grow; challenges like scaling up and keeping their systems running smoothly push them to evolve. Understanding all this shows how these companies adapt and grow in the tech world.
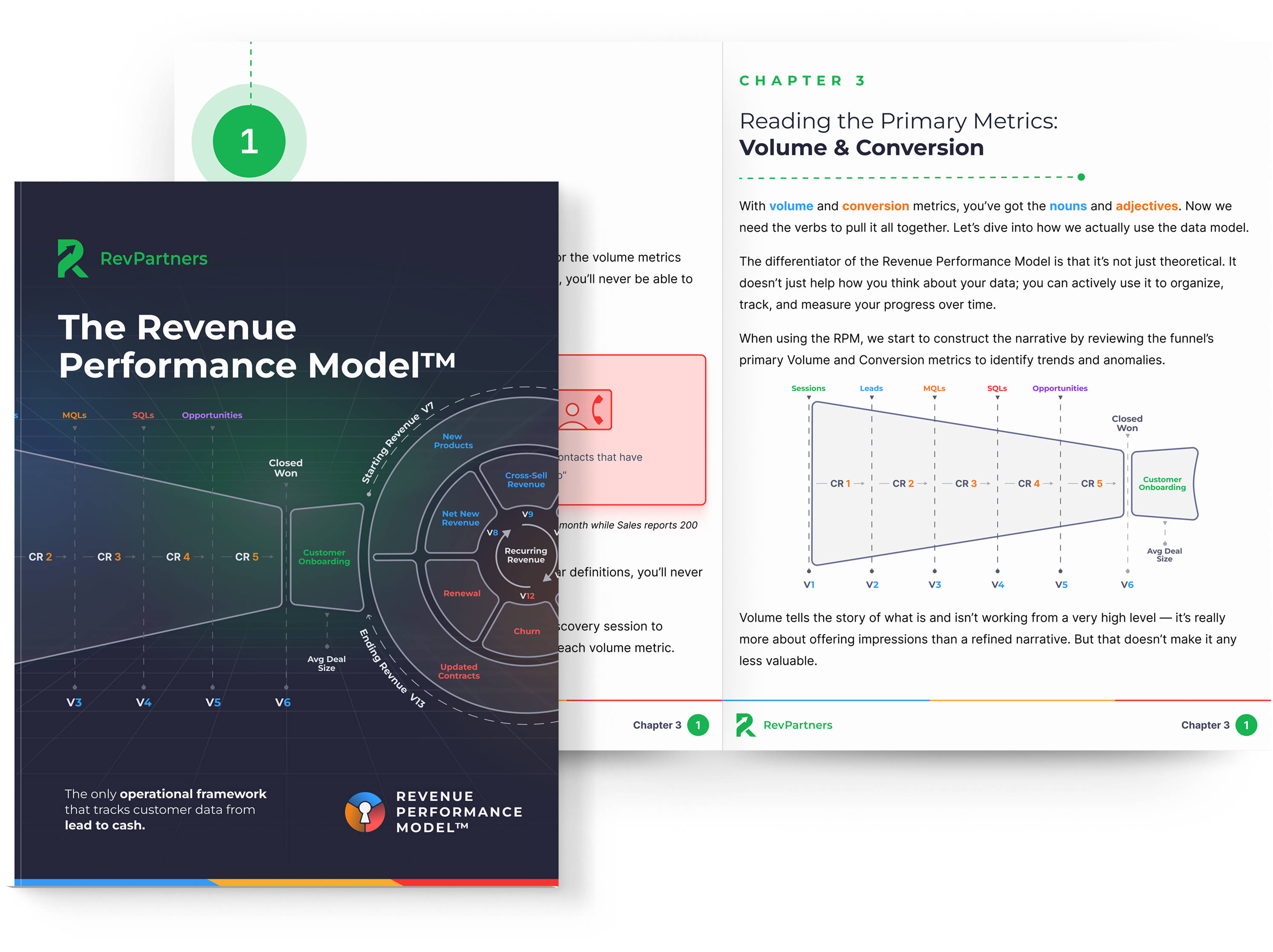
The Revenue Performance Model
Do you want to track the entire revenue journey in your CRM so you can see what's broken, why it happened, and where to fix it?
Download the Revenue Performance Model HERE







-3.png)
.png)
-3.png)